Imagine a world where machines don’t just follow instructions they create, innovate, and dream. Generative AI has transformed this vision into reality, evolving from simple chatbots that answer basic questions to sophisticated creative machines that compose music, design products, write code, and generate photorealistic images. This revolutionary branch of Artificial Intelligence is reshaping industries, redefining creativity, and challenging our understanding of what machines can accomplish. As we navigate through 2025, the power of Generative AI continues to expand, offering unprecedented opportunities for businesses and individuals alike.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Makes Generative AI Different?
At its core, Generative AI uses advanced machine learning models particularly deep learning neural networks, to understand patterns in vast datasets and then generate new outputs that mirror those patterns. The key distinction lies in the word “generative”: these systems don’t simply retrieve or reorganize existing information; they synthesize novel creations.
Traditional AI systems operate on a discriminative model, answering questions like “Is this email spam?” or “What category does this image belong to?” In contrast, Generative AI operates on a generative model, creating responses to prompts like “Write a marketing email” or “Design a logo for a coffee shop.”
The Technology Behind the Magic
Several technological breakthroughs have enabled the rise of Generative AI:
- Transformer Architecture: Introduced in 2017, transformers revolutionized natural language processing by enabling models to understand context and relationships within data more effectively
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): These systems pit two neural networks against each other one generating content and another evaluating it resulting in increasingly realistic outputs
- Diffusion Models: These newer approaches gradually refine random noise into coherent images or other outputs through iterative processes
- Large Language Models (LLMs): Trained on massive text datasets, these models can generate human like text across countless topics and styles
The convergence of these technologies with exponentially growing computational power and data availability has unleashed the creative potential we witness today in Artificial Intelligence systems across industries.
The Evolution: From Simple Chatbots to Creative Powerhouses
The Chatbot Era (2010-2019)
The journey of Generative AI began modestly with rule based chatbots that followed predetermined decision trees. Early systems like ELIZA (1966) and later commercial chatbots could handle basic customer service queries but struggled with anything beyond their programmed responses.
Key Characteristics:
- Limited to scripted conversations
- Unable to handle contextual nuances
- Frequently frustrated users with repetitive responses
- Required extensive manual programming for each scenario
The Breakthrough Period (2020-2022)
The release of GPT-3 in 2020 marked a watershed moment. Suddenly, Artificial Intelligence could engage in remarkably human-like conversations, write coherent essays, and even demonstrate creative writing abilities. Simultaneously, image generation models like DALL E emerged, capable of creating original artwork from text descriptions.
Transformative Capabilities:
- Natural language understanding and generation
- Context awareness across long conversations
- Multi-task versatility without specific training
- Creative output across multiple domains
The Creative Machine Revolution (2023-2025)
Today’s Generative AI systems have transcended their chatbot origins to become true creative machines. Modern platforms can:
- Generate photorealistic images from simple text prompts
- Compose original music in any genre or style
- Write complex code in multiple programming languages
- Create video content with synchronized audio and visuals
- Design presentations with professional layouts and graphics
- Discover new molecular structures for pharmaceutical research
This evolution reflects the transformation detailed in our exploration of how Artificial Intelligence is transforming modern businesses.
Core Applications of Generative AI Across Industries
Content Creation and Marketing
Generative AI has revolutionized content marketing by dramatically accelerating production while maintaining quality. Marketing teams now leverage these tools to:
- Generate blog posts and articles on diverse topics with minimal human input
- Create social media content optimized for different platforms
- Design visual assets including banners, infographics, and advertisements
- Personalize email campaigns at scale with individualized messaging
- Produce video scripts and storyboards for multimedia campaigns
The impact on digital marketing content creation has been particularly profound, enabling smaller teams to compete with larger organizations through enhanced productivity.
Software Development and Programming
Developers have embraced Generative AI as a powerful coding assistant that enhances productivity and reduces errors:
| Application | Benefit | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Code Generation | 40-60% faster development | Writing boilerplate code and functions |
| Bug Detection | Early error identification | Analyzing code for security vulnerabilities |
| Documentation | Automated technical writing | Generating API documentation |
| Code Translation | Cross-language compatibility | Converting Python to JavaScript |
| Testing | Comprehensive test coverage | Creating unit and integration tests |
These capabilities align with modern DevOps best practices by streamlining development workflows and improving code quality.
Creative Industries
Artists, designers, and creative professionals have discovered Generative AI as both a tool and a collaborator:
Visual Arts:
- Concept art generation for games and films
- Style transfer and artistic filters
- Custom illustration creation
- Logo and branding design
Music and Audio:
- Original composition in specific genres
- Background music for videos and podcasts
- Sound effect generation
- Voice synthesis and dubbing
Writing and Literature:
- Story ideation and plot development
- Character dialogue generation
- Poetry and creative writing
- Screenplay drafting
Healthcare and Life Sciences
The medical field has found transformative applications for Generative AI:
- Drug Discovery: Generating molecular structures for potential pharmaceuticals
- Protein Folding: Predicting protein structures to understand diseases
- Clinical Documentation: Automating patient record summaries
- Diagnostic Assistance: Generating differential diagnoses from symptoms
- Treatment Planning: Creating personalized therapy recommendations
Business Operations and Analytics
Organizations leverage Generative AI to optimize operations and extract insights from big data:
- Report Generation: Automatically creating executive summaries from raw data
- Forecasting Models: Generating predictive scenarios for strategic planning
- Customer Service: Handling inquiries with sophisticated conversational AI
- Training Materials: Creating customized learning content for employees
- Process Optimization: Identifying efficiency improvements through data analysis
Real-World Success Stories: Generative AI in Action
Case Study 1: E Commerce Personalization
A major online retailer implemented Generative AI to create personalized product descriptions for millions of items. The system generated unique, SEO optimized descriptions tailored to different customer segments, resulting in:
- 35% increase in organic search traffic
- 22% improvement in conversion rates
- 60% reduction in content creation costs
- Faster time to market for new product listings
Case Study 2: Architectural Design
An architecture firm adopted Generative AI to explore design alternatives for a commercial development project. The AI generated hundreds of layout options optimizing for natural light, energy efficiency, and space utilization, enabling the team to:
- Explore 10x more design variations than traditional methods
- Reduce design iteration time from weeks to days
- Achieve 25% better energy efficiency in the final design
- Win the project bid with innovative solutions
Case Study 3: Customer Support Transformation
A telecommunications company deployed advanced Generative AI chatbots to handle customer inquiries. Unlike previous rule-based systems, these AI agents could understand context, handle complex requests, and even detect customer emotions:
- 70% of inquiries resolved without human intervention
- 40% reduction in average handling time
- 15-point increase in customer satisfaction scores
- 24/7 availability across multiple languages
These examples demonstrate the real-world applications of AI and Generative AI in business environments across diverse sectors.
The Technical Foundation: How Generative AI Works
Training Process
Understanding how Generative AI learns provides insight into both its capabilities and limitations:
Step 1: Data Collection
Models are trained on enormous datasets often containing billions of examples. For language models, this includes books, articles, websites, and conversations. For image generators, millions of images with descriptions.
Step 2: Pattern Recognition
Through deep learning, the neural network identifies patterns, relationships, and structures within the training data. It learns grammar rules, visual composition principles, coding conventions, and domain-specific knowledge.
Step 3: Parameter Optimization
The model adjusts billions of internal parameters (weights) to minimize errors in its predictions. Modern large language models contain hundreds of billions of parameters.
Step 4: Fine-Tuning
Additional training on specific tasks or domains refines the model’s performance for particular applications, such as medical terminology or legal writing.
Generation Process
When you provide a prompt to a Generative AI system:
- Encoding: The input is converted into numerical representations the model can process
- Context Analysis: The model analyzes the prompt’s meaning, intent, and context
- Prediction: Using learned patterns, it predicts the most appropriate next elements (words, pixels, notes)
- Sampling: The model selects from probable options, introducing controlled randomness for creativity
- Decoding: The numerical output is converted back into human readable form
- Iteration: For longer outputs, the process repeats, building on previous generations
Model Architectures
Different Generative AI applications employ specialized architectures:
Transformers (GPT, BERT, T5)
- Excellent for sequential data like text
- Understand long range dependencies
- Enable parallel processing for efficiency
Diffusion Models (Stable Diffusion, DALL E 2)
- Specialized for image generation
- Work by iteratively refining noise into coherent images
- Produce high-quality, detailed outputs
GANs (StyleGAN, CycleGAN)
- Use adversarial training between generator and discriminator
- Excel at realistic image synthesis
- Effective for style transfer applications
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
- Compress data into latent representations
- Useful for generating variations of existing content
- Applied in anomaly detection and data compression
Benefits and Advantages of Generative AI
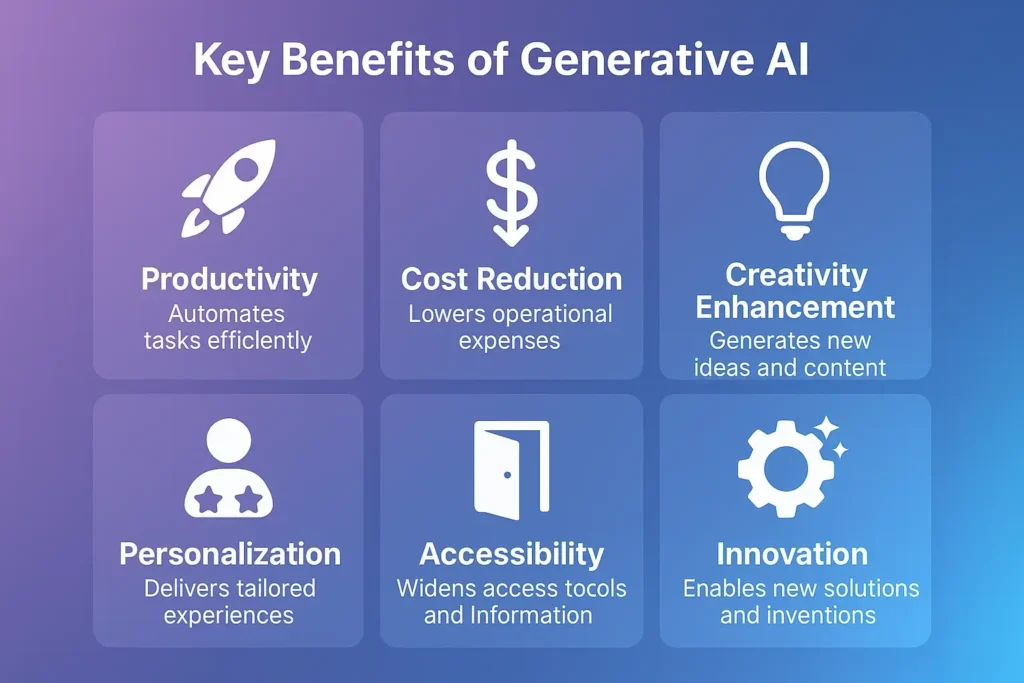
Unprecedented Productivity Gains
Generative AI dramatically accelerates workflows across industries:
- Speed: Tasks that took hours now complete in seconds
- Scalability: Generate thousands of variations without additional resources
- Iteration: Rapidly test and refine ideas with minimal cost
- Consistency: Maintain quality standards across large volumes of output
Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
Organizations implementing Artificial Intelligence & Generative AI report significant cost savings:
- Reduced labor costs for routine content creation
- Lower expenses for stock photography and design assets
- Decreased time to market for new products and campaigns
- Minimized waste through virtual prototyping and testing
Enhanced Creativity and Innovation
Rather than replacing human creativity, Generative AI amplifies it:
“Generative AI serves as a creative partner, offering suggestions and alternatives that spark human imagination and lead to innovations that neither human nor machine could achieve alone.”
- Overcome creative blocks with AI generated starting points
- Explore unconventional solutions beyond traditional thinking
- Combine disparate concepts in novel ways
- Democratize creativity for those without specialized training
Personalization at Scale
Generative AI enables mass customization previously impossible:
- Tailored marketing messages for individual customers
- Personalized learning experiences adapted to each student
- Customized product recommendations based on unique preferences
- Individualized healthcare treatment plans
Accessibility and Democratization
The technology lowers barriers to entry across fields:
- Non-programmers can create functional code
- Writers without design skills can generate professional visuals
- Small businesses can compete with large enterprises
- Non-native speakers can produce polished content in multiple languages
These advantages complement the benefits organizations gain from integrating modern technology practices across their operations.
Challenges and Limitations of Generative AI
Quality and Accuracy Concerns
Despite impressive capabilities, Generative AI faces significant challenges:
Hallucinations: Models sometimes generate plausible-sounding but factually incorrect information with complete confidence. This presents serious risks in fields requiring accuracy like healthcare, law, and journalism.
Inconsistency: Output quality varies unpredictably. The same prompt may produce excellent results one time and poor results another.
Context Limitations: While improving, models still struggle with very long contexts, complex reasoning chains, and nuanced understanding of specialized domains.
Lack of True Understanding: Generative AI operates on pattern matching rather than genuine comprehension, leading to responses that seem intelligent but lack deeper reasoning.
Ethical and Societal Considerations
The rise of Artificial Intelligence & Generative AI raises important ethical questions:
Bias and Fairness
Models trained on historical data inherit societal biases present in that data, potentially perpetuating or amplifying discrimination in:
- Hiring recommendations
- Content moderation decisions
- Creative representations
- Resource allocation
Misinformation and Deepfakes
The ability to generate convincing fake text, images, audio, and video creates risks:
- Political manipulation through synthetic media
- Identity theft and fraud
- Erosion of trust in authentic content
- Difficulty distinguishing real from generated material
Intellectual Property Issues
Unresolved questions about ownership and rights:
- Who owns AI generated content?
- Does training on copyrighted material constitute infringement?
- How should attribution work for AI-assisted creation?
- What protections exist for original creators?
Job Displacement
Automation through Generative AI threatens certain roles:
- Entry-level content writing positions
- Stock photography and illustration
- Basic coding and data entry
- Customer service representatives
Technical Limitations
Current Generative AI systems face inherent constraints:
| Limitation | Impact | Current Status |
|---|---|---|
| Computational Cost | High energy and resource requirements | Improving but still significant |
| Training Data Needs | Requires massive datasets | Techniques like few-shot learning helping |
| Explainability | Difficult to understand decision-making | Active research area |
| Fine Control | Challenging to achieve precise outputs | Better tools emerging |
| Real-time Performance | Latency for complex generations | Optimization ongoing |
Privacy and Security Risks
Generative AI introduces new vulnerabilities:
- Data Leakage: Models might inadvertently reveal training data
- Prompt Injection: Malicious inputs can manipulate model behavior
- Model Theft: Valuable trained models become targets for theft
- Adversarial Attacks: Carefully crafted inputs can fool AI systems
Best Practices for Implementing Generative AI
Strategic Planning and Assessment
Before deploying Generative AI, organizations should:
1. Identify Appropriate Use Cases
- Focus on tasks with clear inputs and outputs
- Prioritize applications where speed and scale matter
- Avoid critical decisions requiring accountability
- Consider areas where human creativity can be augmented
2. Evaluate Readiness
- Assess data availability and quality
- Review technical infrastructure requirements
- Gauge organizational change management capacity
- Understand regulatory and compliance implications
3. Set Realistic Expectations
- Recognize limitations alongside capabilities
- Plan for human oversight and verification
- Budget for ongoing refinement and improvement
- Prepare for iterative deployment rather than perfection
Technical Implementation Guidelines
Choose the Right Model
- Evaluate specialized vs general-purpose models
- Consider open-source vs proprietary solutions
- Balance performance with cost and latency
- Assess customization and fine tuning options
Establish Quality Controls
- Implement human review for critical outputs
- Create validation processes and benchmarks
- Monitor for bias, accuracy, and consistency
- Develop feedback loops for continuous improvement
Ensure Security and Privacy
- Protect sensitive data in training and prompts
- Implement access controls and authentication
- Regular security audits and updates
- Comply with data protection regulations
Optimize Performance
- Fine-tune models for specific domains
- Use prompt engineering for better results
- Cache common queries to reduce costs
- Monitor and optimize computational resources
These implementation approaches align with best practices for modern technology deployment in cloud and distributed environments.
Organizational and Human Factors
Training and Change Management
- Educate teams on capabilities and limitations
- Develop guidelines for appropriate use
- Create communities of practice for sharing insights
- Address concerns about job security and roles
Ethical Frameworks
- Establish clear ethical guidelines for AI use
- Form oversight committees for sensitive applications
- Implement transparency in AI generated content
- Create processes for addressing bias and fairness
Continuous Learning
- Stay current with rapidly evolving technology
- Participate in industry forums and communities
- Experiment with new models and techniques
- Share learnings across the organization
The Future of Generative AI What’s Next?
Emerging Capabilities
The next generation of Generative AI promises even more transformative capabilities:
Multimodal Integration
Future systems will seamlessly work across text, images, audio, video, and 3D environments, understanding and generating content that combines multiple modalities naturally.
Improved Reasoning
Advances in model architecture and training techniques will enhance logical reasoning, mathematical capabilities, and complex problem-solving beyond current pattern-matching approaches.
Personalization and Adaptation
AI systems will better understand individual users, adapting their style, tone, and content to personal preferences while maintaining ethical boundaries.
Real-World Interaction
Integration with robotics and IoT devices will enable Generative AI to interact with and modify the physical world, not just digital content.
Industry Specific Evolution
Different sectors will see specialized Artificial Intelligence & Generative AI developments:
Healthcare
- Personalized treatment protocol generation
- Real time surgical assistance
- Drug discovery acceleration
- Patient education materials
Education
- Adaptive learning systems
- Automated curriculum development
- Virtual tutors and teaching assistants
- Accessibility tools for diverse learners
Manufacturing
- Generative design for products
- Process optimization
- Predictive maintenance
- Supply chain scenario planning
Entertainment
- Interactive storytelling
- Procedurally generated game content
- Virtual world creation
- Personalized media experiences
Regulatory and Governance Trends
As Generative AI matures, expect increased regulation:
- Transparency Requirements: Mandates to disclose AI generated content
- Liability Frameworks: Legal clarity on responsibility for AI outputs
- Safety Standards: Testing and certification for high risk applications
- International Coordination: Global agreements on AI governance
Democratization and Accessibility
The tools will become more accessible:
- Lower cost models for small businesses and individuals
- No code interfaces for non technical users
- Open-source alternatives to proprietary systems
- Educational resources and training programs
The trajectory suggests Generative AI will become as ubiquitous as search engines and smartphones, fundamentally changing how we work, create, and interact with technology. Organizations exploring these possibilities can learn from various AI applications across industries to inform their strategies.
Building a Responsible Generative AI Strategy
Governance Framework
Successful Generative AI adoption requires robust governance:
Policy Development
- Create acceptable use policies
- Define approval processes for different applications
- Establish content review procedures
- Document decision making criteria
Risk Management
- Identify potential harms and mitigation strategies
- Develop incident response plans
- Conduct regular risk assessments
- Maintain audit trails for accountability
Stakeholder Engagement
- Include diverse perspectives in AI decisions
- Communicate transparently about AI use
- Gather feedback from affected parties
- Address concerns proactively
Measuring Success
Define metrics to evaluate Generative AI initiatives:
Quantitative Metrics
- Time savings per task
- Cost reduction percentages
- Output volume increases
- Quality scores and accuracy rates
- User satisfaction ratings
Qualitative Indicators
- Innovation and creativity enhancement
- Employee satisfaction and engagement
- Customer experience improvements
- Competitive advantage gains
- Organizational learning and capability building
Continuous Improvement
Generative AI deployment is not a one time event:
- Regularly update models with new capabilities
- Refine prompts and processes based on experience
- Expand applications as confidence grows
- Share learnings across teams and departments
- Stay informed about emerging best practices
Conclusion: Embracing the Generative AI Revolution
The journey from chatbots to creative machines represents one of the most significant technological transformations of our era. Generative AI has evolved from simple question answering systems to sophisticated creative partners capable of producing original content across virtually every domain of human expression and productivity.
The power of Artificial Intelligence & Generative AI lies not in replacing human creativity and intelligence, but in augmenting and amplifying our capabilities. When implemented thoughtfully, these technologies can:
- Accelerate innovation by rapidly exploring possibilities
- Democratize creativity by making advanced tools accessible to all
- Enhance productivity by automating routine tasks
- Personalize experiences at unprecedented scale
- Solve complex problems through novel approaches
However, this power comes with responsibility. Organizations and individuals must navigate challenges around accuracy, bias, ethics, privacy, and societal impact. Success requires balancing enthusiasm for capabilities with realistic understanding of limitations, implementing robust governance frameworks, and maintaining human oversight for critical decisions.