The world of data engineering is standing at the edge of a revolution. Imagine a future where complex data pipelines build themselves, where data quality issues are detected and resolved before they impact business decisions, and where the bottleneck of manual coding becomes a relic of the past. This isn’t science fiction it’s the imminent reality that artificial intelligence is bringing to the data engineering landscape in 2025 and beyond.
As organizations continue to grapple with exponential data growth, the traditional approaches to data engineering are showing their limitations. The demand for skilled data engineers far outpaces supply, while the complexity of modern data ecosystems continues to escalate. Enter AI: a transformative force that promises to reshape every aspect of how we collect, process, transform, and manage data at scale.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Current State of Data Engineering
Before exploring how AI will disrupt the field, it’s essential to understand where data engineering stands today. Data engineers are the architects and builders of the data infrastructure that powers modern businesses. They design, construct, and maintain the systems that collect, store, transform, and deliver data to analysts, scientists, and business stakeholders.
The Traditional Data Engineering Workflow
The conventional data engineering process involves several labor-intensive stages:
- Data ingestion Extracting data from various sources
- Data transformation Cleaning, normalizing, and structuring raw data
- Data storage Organizing data in databases and data warehouses
- Data pipeline orchestration Managing the flow of data through systems
- Quality assurance Monitoring and validating data accuracy
- Performance optimization Tuning queries and infrastructure for efficiency
Each of these stages requires significant manual effort, deep technical expertise, and constant monitoring. The complexity multiplies as organizations deal with diverse data sources, increasing volumes, and stringent compliance requirements.
Current Challenges Facing Data Engineers
Data engineers today face a perfect storm of challenges:
| Challenge | Impact | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Data quality issues | Incorrect business decisions | 60% of projects |
| Pipeline failures | Delayed insights and reporting | 45% experience weekly |
| Scalability bottlenecks | Slow query performance | 55% of organizations |
| Technical debt | Increased maintenance costs | 70% of legacy systems |
| Skill shortages | Project delays and backlogs | 80% of companies |
These challenges are compounded by the fact that big data continues to grow exponentially, with organizations now managing petabytes of information across cloud and on premises environments.
The AI Revolution in Data Engineering
Artificial intelligence is not just another tool in the data engineer’s toolkit it represents a fundamental paradigm shift in how data engineering work gets done. The transformation is happening across multiple dimensions simultaneously.
Automated Pipeline Generation and Management
One of the most significant disruptions AI brings is the ability to automatically generate and manage data pipelines. Traditional pipeline creation requires data engineers to manually write code, define transformations, and configure orchestration. AI-powered tools are changing this:
- Natural language to pipeline: Engineers can describe their requirements in plain English, and AI generates the corresponding pipeline code
- Auto-optimization: Machine learning algorithms continuously monitor pipeline performance and automatically adjust configurations for optimal efficiency
- Predictive maintenance: AI predicts potential pipeline failures before they occur, enabling proactive fixes
This shift means that artificial intelligence is transforming modern businesses not just at the application layer, but at the fundamental data infrastructure level.
Intelligent Data Quality and Governance
Data quality has long been one of the most time-consuming aspects of data engineering. AI is revolutionizing this domain through:
Automated anomaly detection
- Pattern recognition algorithms identify unusual data patterns that might indicate quality issues
- Contextual understanding of what “normal” looks like for specific data types
- Real-time alerts when data deviates from expected patterns
Smart data profiling
- AI automatically generates comprehensive data quality reports
- Identifies relationships between fields that humans might miss
- Suggests appropriate data types, constraints, and validation rules
Intelligent data lineage
- Automatic tracking of data flow through complex systems
- Visual representation of data transformations and dependencies
- Impact analysis showing downstream effects of data changes
Self-Optimizing Data Infrastructure
Perhaps the most transformative aspect of AI in data engineering is the emergence of self optimizing infrastructure. Modern AI systems can:
- Automatically partition data based on access patterns
- Dynamically allocate resources to handle varying workloads
- Optimize query execution plans better than human-written code
- Predict storage needs and provision capacity proactively
- Balance cost and performance based on business priorities
This level of automation mirrors the best practices for DevOps in cloud environments, where infrastructure becomes increasingly self-managing and adaptive.
How AI Tools Are Changing Daily Data Engineering Tasks
The practical impact of AI on day to day data engineering work is already visible in 2025. Let’s examine specific tasks and how they’re being transformed.
Data Integration and ETL
Before AI:
- Manually writing connectors for each data source
- Creating custom transformation logic for every use case
- Hours spent debugging integration issues
- Constant maintenance as source systems change
With AI:
- AI-powered connectors that auto adapt to schema changes
- Automatic mapping suggestions between source and target systems
- Intelligent error handling and retry logic
- Self-documenting integration flows
Data Modeling and Schema Design
AI assistants now help data engineers design optimal database schemas by:
- Analyzing query patterns to suggest appropriate indexing strategies
- Recommending normalization or denormalization based on use cases
- Automatically generating dimensional models from source data
- Predicting future storage and performance requirements
Code Generation and Documentation
Modern AI coding assistants have become indispensable partners for data engineers:
- Generate SQL queries from natural language descriptions
- Write Python/Scala code for data transformations
- Create unit tests automatically for data pipelines
- Generate comprehensive documentation from code
- Suggest performance improvements in existing code
This represents a fundamental shift similar to how generative AI is transforming digital marketing, but applied to the technical domain of data infrastructure.
The Evolution of Data Engineering Jobs
A common concern is whether AI will eliminate data engineering jobs. The reality is more nuanced and actually more optimistic than many fear.
From Builders to Architects and Strategists
The role of data engineers is evolving from hands on builders to strategic architects who:
Design high level data strategies
- Define organizational data architecture principles
- Make critical decisions about technology stack and platforms
- Align data infrastructure with business objectives
Supervise and guide AI systems
- Train AI models on organizational specific requirements
- Validate AI-generated solutions for correctness and efficiency
- Fine-tune automated systems for optimal performance
Focus on complex problem solving
- Address edge cases and unique challenges that AI can’t handle
- Design solutions for novel business requirements
- Innovate new approaches to emerging data challenges
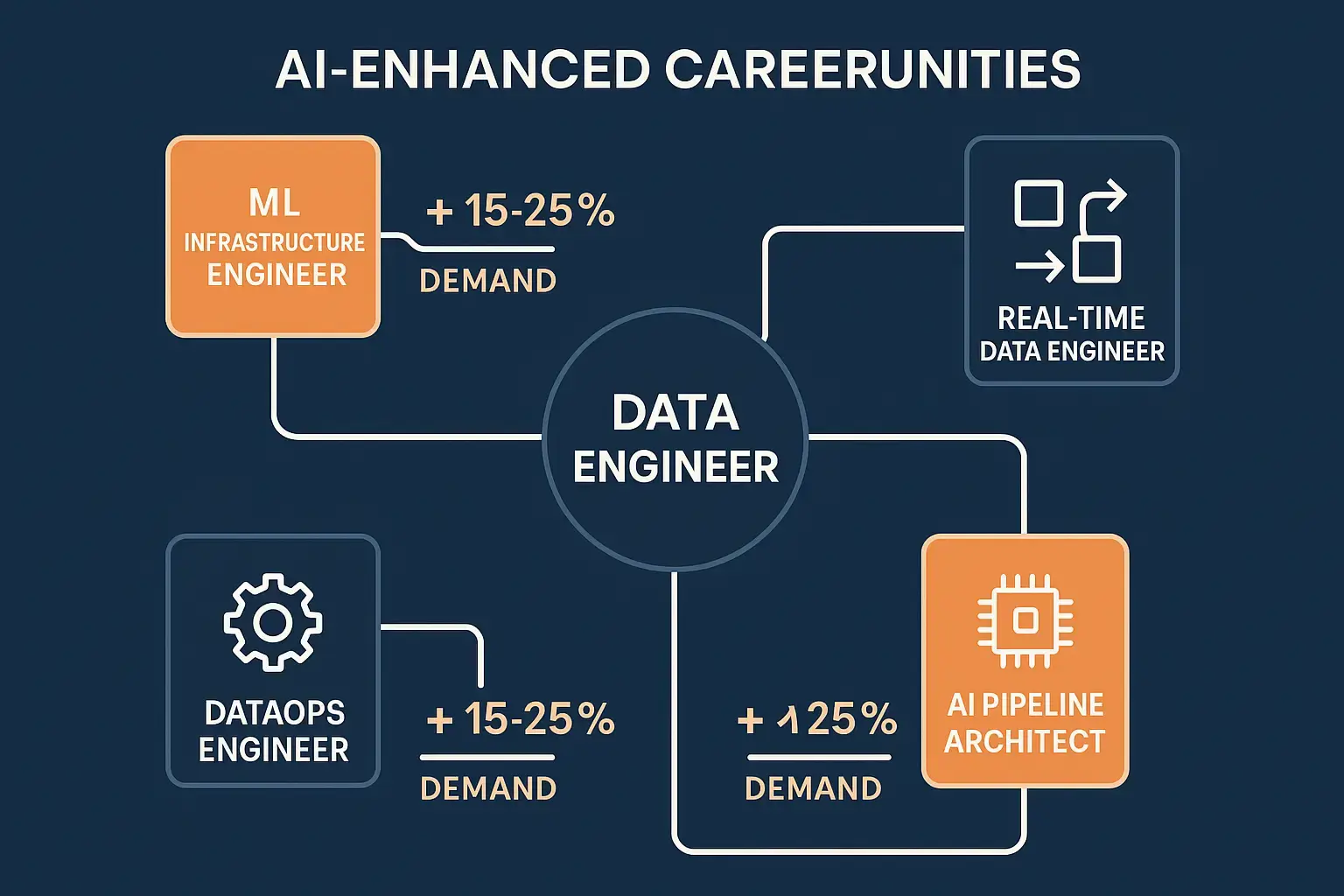
New Skills for the AI Era
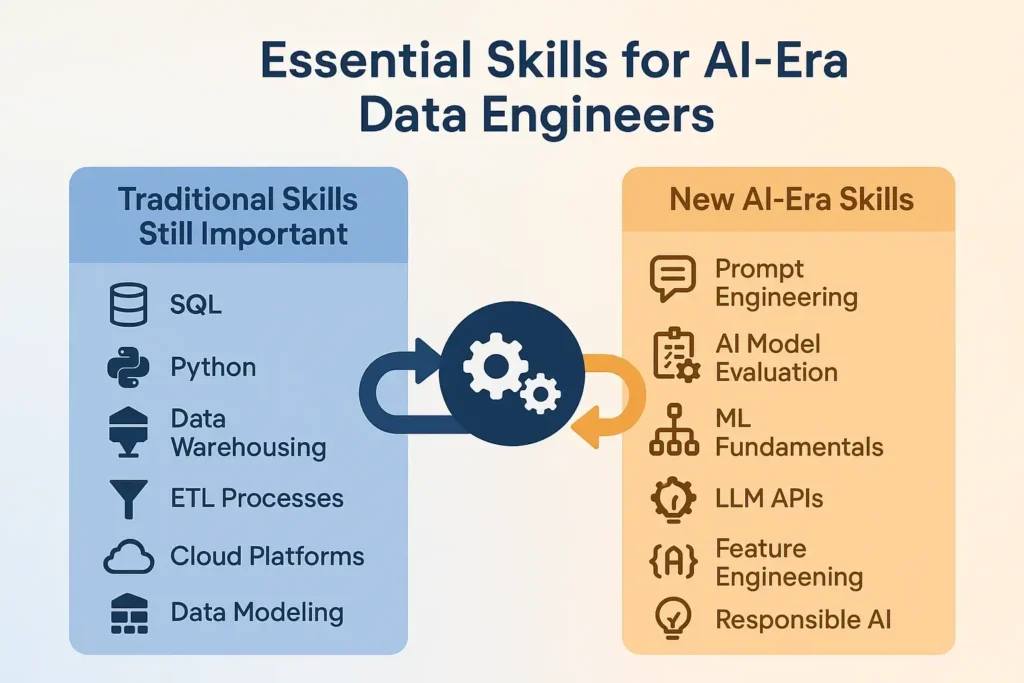
The skill set required for data engineers is shifting. While traditional technical skills remain important, new competencies are becoming critical:
| Traditional Skills | Emerging AI-Era Skills |
|---|---|
| SQL and database design | Prompt engineering for AI tools |
| Python/Java programming | AI model evaluation and selection |
| ETL tool expertise | AI system monitoring and governance |
| Data warehouse architecture | Hybrid human-AI workflow design |
| Performance tuning | AI ethics and bias detection |
Job Market Transformation
Rather than eliminating jobs, AI is creating new categories of roles:
- AI Data Engineers: Specialists who build and maintain AI powered data infrastructure
- Data Pipeline Architects: Strategic designers of complex data ecosystems
- Data Governance Specialists: Experts ensuring AI-generated data solutions meet compliance and quality standards
- MLOps Engineers: Professionals managing the intersection of data engineering and machine learning
The top 10 real-world applications of AI in business demonstrate that AI creates as many opportunities as it transforms.
Real-World Examples of AI Disrupting Data Engineering
Let’s examine concrete examples of how organizations are already leveraging AI to transform their data engineering practices.
Case Study: Automated Data Warehouse Modernization
A major retail company used AI to migrate their legacy data warehouse to a modern cloud platform:
- Challenge: 15 years of accumulated technical debt, thousands of ETL jobs, undocumented transformations
- AI Solution: Machine learning algorithms analyzed existing code, automatically generated modern equivalents, and created comprehensive documentation
- Result: Migration completed in 6 months instead of projected 3 years, with 95% automation rate
Case Study: Intelligent Data Quality Management
A healthcare provider implemented AI powered data quality monitoring:
- Challenge: Patient data coming from 50+ systems with inconsistent quality, impacting care decisions
- AI Solution: Deep learning models learned normal patterns for each data type, automatically flagging anomalies
- Result: Data quality issues detected 80% faster, with 90% reduction in false positives
Case Study: Self-Optimizing Data Lakehouse
A financial services firm deployed AI to manage their data lakehouse:
- Challenge: Unpredictable query performance, manual tuning taking weeks
- AI Solution: Reinforcement learning system that continuously optimized data layout, partitioning, and caching
- Result: 60% improvement in average query performance, 40% reduction in infrastructure costs
These examples align with broader trends in AI driving innovation across industries, showing that data engineering is just one of many fields being transformed.
The Technical Architecture of AI-Powered Data Engineering
Understanding how AI integrates into data engineering requires examining the technical architecture that makes it possible.
The AI-Native Data Stack
Modern AI-powered data engineering platforms typically include:
Intelligent Orchestration Layer
- AI-driven workflow scheduling based on data availability and priority
- Automatic dependency resolution and parallel execution optimization
- Predictive resource allocation
Smart Processing Engine
- Auto-scaling compute resources based on workload
- Intelligent caching and materialization strategies
- Query optimization using machine learning
Adaptive Storage Layer
- Automatic data tiering based on access patterns
- Smart compression and encoding selection
- Predictive pre fetching for frequently accessed data
Autonomous Monitoring System
- Real-time anomaly detection across all data pipelines
- Automated root cause analysis for failures
- Self-healing capabilities for common issues
Integration with Existing Infrastructure
AI doesn’t require a complete rip-and-replace of existing data infrastructure. Instead, it augments current systems through:
- API-based integration with existing data tools
- Metadata-driven learning from current pipeline configurations
- Gradual adoption allowing teams to start with specific use cases
- Hybrid approaches combining human expertise with AI automation
This integration philosophy mirrors DevOps best practices, emphasizing incremental improvement and continuous evolution.
Challenges and Considerations in AI-Driven Data Engineering
While the benefits are substantial, organizations must navigate several challenges when adopting AI for data engineering.
Trust and Validation
“The biggest challenge isn’t getting AI to generate code it’s ensuring that generated code is correct, efficient, and maintainable.” Senior Data Engineering Leader
Key considerations:
- Establishing validation frameworks for AI-generated solutions
- Building confidence through gradual adoption and testing
- Maintaining human oversight for critical data pipelines
- Creating audit trails for AI decisions
Skill Gap and Training
Organizations face the challenge of upskilling their existing data engineering teams:
- Resistance to change: Some engineers may be skeptical of AI assistance
- Learning curve: New tools and approaches require training investment
- Knowledge transfer: Ensuring institutional knowledge isn’t lost to automation
- Hiring challenges: Finding engineers with both traditional and AI skills
Data Privacy and Security
AI systems require access to data to learn and optimize, raising important questions:
- How to train AI models without exposing sensitive data?
- Ensuring AI-generated code complies with data regulations
- Preventing AI systems from inadvertently creating security vulnerabilities
- Maintaining data lineage and governance in AI-automated environments
Cost and ROI Considerations
While AI promises efficiency gains, organizations must consider:
- Initial investment in AI platforms and tools
- Training costs for teams
- Ongoing subscription fees for AI services
- Potential savings from automation and efficiency
- Value of faster time to insight
Preparing for the AI-Driven Future of Data Engineering
Organizations and individuals can take concrete steps to prepare for this transformation.
For Organizations
1. Assess Current Capabilities
- Audit existing data engineering processes
- Identify repetitive, automatable tasks
- Evaluate team readiness for AI adoption
2. Start with Pilot Projects
- Choose low risk, high value use cases
- Measure results rigorously
- Learn and iterate before scaling
3. Invest in Training
- Provide AI literacy training for data teams
- Offer hands on experience with AI tools
- Create internal communities of practice
4. Establish Governance Frameworks
- Define standards for AI-generated code
- Create review processes for automated solutions
- Ensure compliance and security requirements are met
5. Build Strategic Partnerships
- Collaborate with AI platform vendors
- Join industry consortiums sharing best practices
- Engage with the broader data engineering community
Similar to integrating DevOps with cloud services, successful AI adoption requires strategic planning and organizational alignment.
For Data Engineering Professionals
Embrace Continuous Learning
- Stay current with emerging AI tools and platforms
- Experiment with AI coding assistants
- Understand machine learning fundamentals
Develop Strategic Thinking
- Focus on architecture and design skills
- Learn to articulate business value of data initiatives
- Develop stakeholder communication abilities
Build AI Collaboration Skills
- Learn effective prompt engineering
- Understand how to validate AI outputs
- Practice human-AI paired programming
Specialize Strategically
- Identify niche areas where human expertise remains critical
- Develop deep domain knowledge in specific industries
- Build expertise in AI governance and ethics
The Future Landscape: 2025 and Beyond

Looking ahead, several trends will shape the continued evolution of AI in data engineering.
Predictions for the Next Five Years
2025-2026: Mainstream Adoption
- AI coding assistants become standard tools for all data engineers
- First generation of fully autonomous data pipelines in production
- Emergence of AI-specific data engineering certifications
2027-2028: Advanced Automation
- 70% of routine data engineering tasks automated
- AI systems handling end to end data product development
- Natural language interfaces for complex data operations
2029-2030: Intelligent Data Ecosystems
- Self evolving data architectures that adapt to business changes
- AI to AI collaboration between data systems
- Quantum computing integration for complex data processing
Emerging Technologies to Watch
- Quantum Machine Learning: Solving previously impossible optimization problems in data engineering
- Neuromorphic Computing: More efficient AI processing for real time data transformation
- Federated Learning: Training AI models across distributed data sources without centralization
- Edge AI: Intelligent data processing at the source, reducing latency and bandwidth
The Human Element Remains Critical
Despite increasing automation, human data engineers will remain essential for:
- Creative problem-solving: Addressing novel challenges that AI hasn’t encountered
- Ethical oversight: Ensuring AI systems align with organizational values and societal norms
- Strategic vision: Defining what data capabilities the organization needs
- Cross-functional collaboration: Bridging technical and business stakeholders
- Innovation: Pushing boundaries of what’s possible with data
For more insights on the broader impact of these technologies, explore how generative AI is transforming digital marketing and other business functions.
Best Practices for Implementing AI in Data Engineering
Organizations looking to successfully integrate AI into their data engineering workflows should follow these proven best practices.
Start Small and Scale Gradually
Rather than attempting a complete transformation overnight, successful organizations:
- Identify quick wins: Choose use cases with clear ROI and manageable complexity
- Run pilot programs: Test AI tools in controlled environments before production deployment
- Measure rigorously: Track metrics like time saved, error reduction, and cost impact
- Iterate based on feedback: Continuously refine approaches based on team input
Build a Culture of Experimentation
Creating an environment where data engineers feel empowered to experiment with AI is crucial:
- Allocate innovation time: Dedicate 10 20% of team capacity to exploring new AI tools
- Celebrate learning: Reward both successes and intelligent failures
- Share discoveries: Create forums for teams to share AI experiments and learnings
- Remove barriers: Provide easy access to AI tools and training resources
Maintain Human Oversight
Even as automation increases, human judgment remains essential:
- Establish review processes: Define when and how humans validate AI outputs
- Create escalation paths: Ensure complex or unusual cases get human attention
- Monitor AI decisions: Track patterns in AI-generated solutions to identify biases or errors
- Preserve institutional knowledge: Document why certain architectural decisions were made
Invest in the Right Tools
Not all AI tools are created equal. Evaluate options based on:
| Evaluation Criteria | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Integration capabilities | Must work with existing data stack |
| Transparency | Ability to understand AI reasoning |
| Customization | Adapt to organizational requirements |
| Support and community | Access to help and best practices |
| Security and compliance | Meet regulatory requirements |
| Total cost of ownership | Licensing, training, maintenance costs |
Prioritize Data Security and Governance
As AI systems gain access to more data and decision-making authority:
- Implement role based access controls for AI tools
- Ensure data anonymization when training AI models
- Maintain comprehensive audit logs of AI actions
- Establish clear accountability for AI-generated outputs
- Create incident response plans for AI-related issues
These practices align with the broader principles outlined in DevOps best practices, emphasizing automation with appropriate controls.
The Broader Impact on the Data Ecosystem
The AI disruption in data engineering doesn’t exist in isolation it’s part of a broader transformation affecting the entire data ecosystem.
Impact on Adjacent Roles
Data Scientists
- More time for advanced analytics as data preparation becomes automated
- Easier access to clean, well structured data
- Collaboration with AI systems for feature engineering
Data Analysts
- Self service access to complex data without engineering support
- AI generated insights and anomaly detection
- Natural language interfaces for data queries
Business Users
- Direct access to data through AI powered interfaces
- Faster time-to-insight for business questions
- Reduced dependency on technical teams for standard reports
Changes in Organizational Structure
Forward-thinking organizations are restructuring their data teams:
- Centralized AI enablement teams: Specialists who help all data teams leverage AI
- Embedded AI engineers: AI experts working within product teams
- Data product managers: Roles focused on defining and delivering data capabilities
- Cross-functional squads: Mixed teams of engineers, scientists, and business experts
Evolution of Data Governance
AI introduces new governance challenges and opportunities:
Challenges:
- Ensuring AI-generated code meets quality standards
- Tracking lineage through AI transformations
- Managing AI model drift and updates
- Auditing automated decisions
Opportunities:
- Automated policy enforcement
- Intelligent data classification and tagging
- Proactive compliance monitoring
- Self-documenting data systems
Economic Implications of AI in Data Engineering
The economic impact of AI disruption in data engineering extends far beyond individual organizations.
Market Size and Growth
The AI-powered data engineering tools market is experiencing explosive growth:
- 2025 Market Size: $8.5 billion
- Projected 2030 Size: $42 billion
- CAGR: 38% (2025-2030)
- Key drivers: Cloud adoption, data volume growth, talent shortage
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Organizations implementing AI in data engineering typically see:
Costs:
- Tool licensing: $50-500 per user/month
- Training and change management: $100,000-500,000
- Infrastructure upgrades: Variable based on scale
- Ongoing optimization: 10-15% of implementation cost annually
Benefits:
- 40-60% reduction in routine development time
- 30-50% decrease in data quality issues
- 20-30% lower infrastructure costs through optimization
- 2-3x faster time-to-market for new data products
Typical ROI: 200-400% within 18-24 months
Impact on Salaries and Compensation
Interestingly, AI is not depressing data engineering salaries quite the opposite:
- Traditional data engineers: $110,000-160,000 average
- AI-enabled data engineers: $130,000-190,000 average
- AI data engineering specialists: $150,000-220,000 average
The premium reflects the increased value these professionals deliver when augmented by AI tools, similar to trends seen across various industries adopting AI.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible AI Use
As AI becomes more prevalent in data engineering, ethical considerations become increasingly important.
Bias in AI-Generated Solutions
AI systems can perpetuate or amplify biases present in training data:
- Recognition: Understand that AI tools may suggest biased approaches
- Testing: Rigorously test AI-generated code for fairness and equity
- Diversity: Ensure training data represents diverse scenarios
- Transparency: Document AI involvement in critical data pipelines
Job Displacement Concerns
While we’ve discussed job evolution, organizations have ethical obligations:
- Reskilling programs: Invest in helping affected employees transition
- Transparent communication: Be honest about changes and timelines
- Gradual transitions: Avoid sudden, disruptive changes
- Support systems: Provide resources for career development
Environmental Impact
AI systems consume significant computational resources:
- Energy efficiency: Choose AI tools optimized for energy consumption
- Carbon awareness: Run training and inference during low-carbon periods
- Right-sizing: Use appropriate AI model sizes for tasks
- Monitoring: Track and report environmental impact of AI usage
Data Privacy and Consent
AI tools often require access to data for training and optimization:
- Ensure clear consent for data usage in AI training
- Implement data minimization principles
- Respect regional regulations (GDPR, CCPA, etc.)
- Provide opt out mechanisms where appropriate
Conclusion: Embracing the AI-Driven Future
The disruption of data engineering by artificial intelligence is not a distant possibility it’s happening right now in 2025. Organizations and professionals who recognize this transformation and adapt proactively will thrive, while those who resist will find themselves increasingly unable to compete.
The future of data engineering is not about humans versus machines, but rather humans augmented by machines. AI will handle the repetitive, time-consuming tasks that have long burdened data engineers, freeing them to focus on strategic thinking, creative problem-solving, and delivering business value