The digital landscape is shifting faster than ever before. In 2025, businesses that fail to adapt their cloud infrastructure and DevOps practices risk falling behind competitors who embrace innovation. As organizations worldwide accelerate their digital transformation journeys, the convergence of cloud computing and DevOps has become not just a competitive advantage, but a necessity for survival in an increasingly automated, AI driven marketplace.
The evolution of DevOps cloud services has fundamentally transformed how businesses build, deploy, and scale applications. What started as a methodology to bridge the gap between development and operations teams has evolved into a sophisticated ecosystem of tools, practices, and cultural shifts that define modern software delivery. Companies investing in cloud devops consulting services are discovering unprecedented levels of agility, efficiency, and innovation capacity.
This comprehensive guide explores the critical trends shaping the future of cloud and DevOps, providing business leaders, IT decision-makers, and technology professionals with actionable insights to navigate this rapidly evolving landscape.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Cloud DevOps Convergence
The marriage between cloud computing and DevOps represents one of the most significant technological partnerships of the modern era. This convergence has created an environment where cloud devops engineering services can deliver unprecedented value to organizations of all sizes.
What Makes Cloud and DevOps Inseparable?
Cloud platforms provide the infrastructure flexibility that DevOps practices require. Traditional on premises environments often created bottlenecks in the deployment pipeline, but cloud infrastructure offers:
- Elastic scalability that matches DevOps’ rapid deployment cycles
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) capabilities that enable version-controlled infrastructure
- API-driven automation that integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines
- Pay-as-you-go models that align with DevOps’ experimental and iterative approach
The synergy between these technologies has led to the rise of specialized cloud devops service providers who help organizations maximize this potential. Companies leveraging these services report 60% faster time to market and 50% reduction in infrastructure costs compared to traditional approaches.
Trend #1: AI and Machine Learning Integration in DevOps
Artificial intelligence is no longer a futuristic concept it’s actively reshaping DevOps workflows in 2025. The integration of AI and ML into DevOps practices, often called AIOps, represents a paradigm shift in how teams manage complex cloud environments.
Intelligent Automation Beyond Scripts
Traditional automation relied on predefined scripts and rules. AI powered DevOps tools now:
- Predict infrastructure failures before they occur by analyzing patterns in logs and metrics
- Automatically optimize resource allocation based on usage patterns and cost constraints
- Identify security vulnerabilities using machine learning models trained on millions of code repositories
- Generate deployment strategies that minimize risk based on historical success rates
Organizations implementing AI-driven innovation in their DevOps practices are experiencing transformative results. One major e commerce platform reduced deployment failures by 80% using AI powered predictive analytics.
Self-Healing Systems
The concept of self healing infrastructure has moved from theory to reality. Modern cloud devops engineering services now include:
| Self-Healing Capability | Business Impact | Adoption Rate (2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Automatic rollback on anomaly detection | 95% reduction in downtime | 67% |
| Predictive scaling before traffic spikes | 40% cost optimization | 54% |
| Automated security patch deployment | 85% faster vulnerability remediation | 71% |
| Intelligent log analysis and issue resolution | 60% reduction in MTTR | 48% |
These capabilities are becoming standard offerings in comprehensive cloud devops consulting services, enabling businesses to maintain 99.99% uptime with smaller operational teams.
Trend #2: Multi Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies
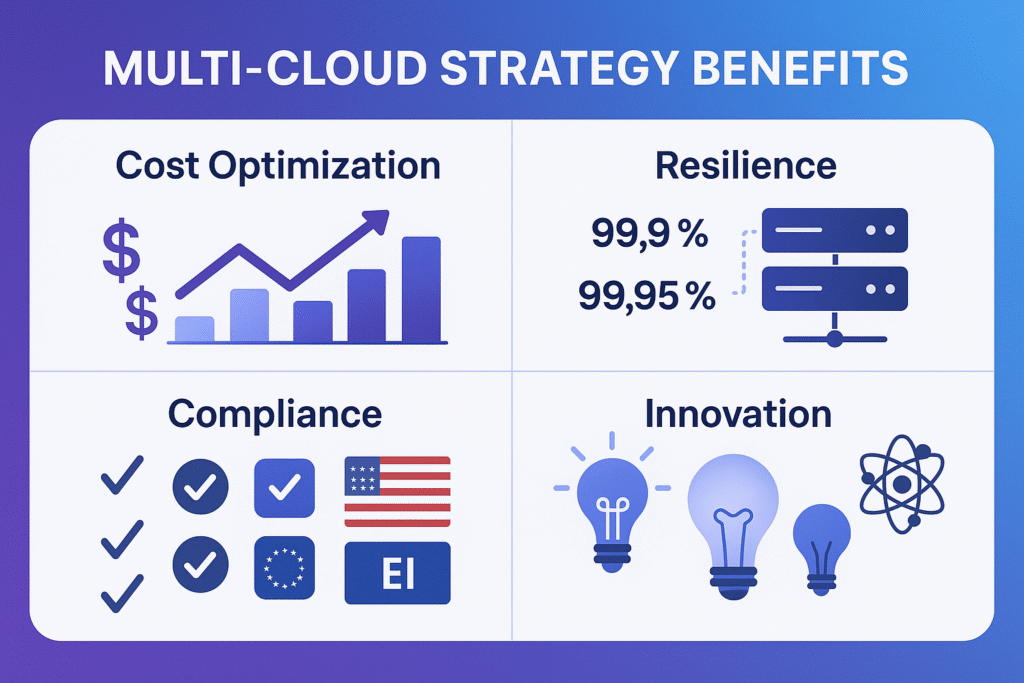
The debate between single cloud and multi cloud approaches has been decisively settled in 2025: flexibility wins. Organizations are increasingly adopting multi cloud and hybrid strategies to avoid vendor lock in, optimize costs, and leverage best of breed services.
The Rise of Cloud Agnostic DevOps
Modern businesses require cloud devops service solutions that work seamlessly across AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and private data centers. This shift has driven the development of:
- Kubernetes and containerization as universal deployment platforms
- Terraform and cloud agnostic IaC tools that manage resources across providers
- Service mesh technologies that enable consistent networking across environments
- Unified observability platforms that provide single-pane-of-glass monitoring
Strategic Advantages of Multi Cloud DevOps
Organizations implementing multi-cloud DevOps strategies report several key benefits:
Cost Optimization: By distributing workloads across providers based on pricing models, companies achieve 30-40% cost savings compared to single-cloud deployments.
Resilience and Redundancy: Geographic distribution across multiple cloud providers creates true disaster recovery capabilities, with some organizations achieving sub-minute failover times.
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions and industries have varying data sovereignty requirements. Multi-cloud strategies enable businesses to keep data in compliant locations while maintaining operational efficiency.
Innovation Access: Each cloud provider excels in different areas AWS for breadth of services, Azure for enterprise integration, Google Cloud for data analytics and AI. Multi cloud approaches let organizations leverage these strengths simultaneously.
Companies seeking to implement these strategies often partner with specialized cloud DevOps consulting services that provide expertise across multiple platforms.
Trend #3: Security First DevOps (DevSecOps)
Security breaches cost organizations an average of $4.45 million in 2025, making security integration into DevOps workflows not just advisable but essential. The shift to DevSecOps represents a fundamental rethinking of when and how security is addressed in the software development lifecycle.
Shifting Security Left
Traditional approaches treated security as a final checkpoint before deployment. DevSecOps integrates security from the earliest stages:
- Security scanning in IDE environments that catch vulnerabilities as code is written
- Automated security testing in CI/CD pipelines that block insecure code from progressing
- Container image scanning that identifies vulnerabilities before deployment
- Runtime security monitoring that detects and responds to threats in production
Zero Trust Architecture in Cloud DevOps
The zero trust security model has become the standard for cloud devops engineering services. Key principles include:
Never Trust, Always Verify: Every request, whether from inside or outside the network, requires authentication and authorization.
Least Privilege Access: Users and services receive only the minimum permissions necessary for their functions, with time-limited credentials becoming the norm.
Micro-Segmentation: Network segmentation at the workload level prevents lateral movement of threats.
Continuous Monitoring: Real-time analysis of all network traffic, user behavior, and system activities to detect anomalies.
Organizations implementing comprehensive DevSecOps practices report 70% fewer security incidents and 65% faster remediation times when issues do occur. For businesses looking to strengthen their security posture, exploring DevOps best practices provides a solid foundation.
Trend #4: Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Evolution
Infrastructure as Code has matured from a novel approach to an industry standard. In 2025, IaC represents the backbone of modern cloud devops service delivery, enabling teams to manage complex infrastructure with the same rigor as application code.
Beyond Basic Automation
Modern IaC practices extend far beyond simple resource provisioning:
Policy as Code: Organizations now codify compliance requirements, security policies, and governance rules that automatically validate infrastructure changes before deployment.
GitOps Workflows: Infrastructure changes follow the same pull request, review, and approval processes as application code, creating comprehensive audit trails and enabling easy rollbacks.
Immutable Infrastructure: Rather than updating existing resources, teams deploy entirely new infrastructure versions, eliminating configuration drift and ensuring consistency.
Testing Infrastructure Code: Infrastructure changes undergo automated testing in isolated environments before affecting production systems.
Popular IaC Tools and Their Evolution
The IaC landscape has consolidated around several key platforms:
- Terraform: Dominant for multi cloud infrastructure management, with enhanced state management and module registries
- AWS CloudFormation: Deeply integrated with AWS services, offering native resource support
- Pulumi: Enables infrastructure definition using general purpose programming languages
- Ansible: Excels at configuration management and application deployment
- Crossplane: Emerging as a Kubernetes-native infrastructure management solution
Companies adopting comprehensive IaC practices through cloud devops consulting services report 80% reduction in infrastructure provisioning time and 90% decrease in configuration-related incidents.
Trend #5: Observability and AIOps
Traditional monitoring tools that simply track metrics and generate alerts are no longer sufficient for complex cloud environments. Observability the ability to understand system behavior from external outputs has become the new standard, enhanced by AI-powered analytics.
The Three Pillars of Observability
Modern observability platforms integrate three critical data types:
Metrics: Numerical measurements of system performance (CPU usage, request rates, error counts) collected at regular intervals.
Logs: Detailed records of discrete events within applications and infrastructure, now structured for machine analysis.
Traces: Complete journey maps of requests as they flow through distributed systems, identifying bottlenecks and dependencies.
AIOps: Intelligence Driven Operations
AIOps platforms apply machine learning to observability data, delivering capabilities that were impossible with traditional tools:
- Anomaly Detection: Automatically identifying unusual patterns that indicate problems, even when they don’t cross predefined thresholds
- Root Cause Analysis: Correlating events across multiple systems to pinpoint the source of issues within seconds
- Predictive Alerting: Warning teams about potential problems before they impact users
- Intelligent Noise Reduction: Filtering thousands of alerts down to the few that require human attention
Organizations implementing advanced observability and AIOps through cloud devops engineering services reduce mean time to resolution (MTTR) by an average of 65% and decrease alert fatigue by 80%.
The integration of artificial intelligence in modern business operations extends well beyond DevOps, creating opportunities for holistic digital transformation.
Trend #6: Serverless and Event Driven Architectures
Serverless computing represents the logical evolution of cloud abstraction removing server management entirely from developer concerns. In 2025, serverless has matured beyond simple functions to support complex, event driven architectures.
The Serverless Advantage
Serverless platforms offer compelling benefits that align perfectly with DevOps principles:
Zero Infrastructure Management: Developers focus exclusively on code while cloud providers handle provisioning, scaling, patching, and maintenance.
Automatic Scaling: Applications scale from zero to thousands of concurrent executions without configuration, paying only for actual compute time.
Faster Development Cycles: Reduced operational overhead enables teams to iterate more rapidly, deploying updates multiple times per day.
Cost Efficiency: Pay per execution pricing models eliminate costs for idle resources, reducing expenses by 60 80% for variable workloads.
Event-Driven Architecture Patterns
Modern serverless applications leverage event driven patterns that enable:
- Asynchronous Processing: Decoupling components for improved resilience and scalability
- Real Time Data Processing: Responding to events as they occur across distributed systems
- Microservices Communication: Loosely coupled services that communicate through event buses
- Complex Workflow Orchestration: Multi step processes that span multiple services and platforms
Organizations adopting serverless architectures through specialized cloud devops service providers report 70% reduction in operational overhead and 50% faster feature delivery.
Trend #7: Edge Computing and Distributed Cloud
The proliferation of IoT devices, 5G networks, and latency-sensitive applications has driven the rise of edge computing. In 2025, edge infrastructure is being seamlessly integrated with centralized cloud platforms, creating distributed cloud architectures that extend DevOps practices to the network edge.
Why Edge Computing Matters
Traditional cloud architectures centralize computing in regional data centers, creating latency challenges for certain applications:
Real Time Requirements: Autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and AR/VR applications require sub-10ms response times impossible with centralized clouds.
Bandwidth Optimization: Processing data at the edge reduces the volume of information transmitted to central clouds, lowering costs and improving efficiency.
Privacy and Compliance: Local data processing enables compliance with data sovereignty regulations without sacrificing functionality.
Reliability: Edge processing continues during network disruptions, ensuring critical applications remain operational.
DevOps at the Edge
Extending DevOps practices to edge infrastructure presents unique challenges:
- Deployment at Scale: Managing thousands of edge locations requires sophisticated automation and orchestration
- Resource Constraints: Edge devices often have limited compute and storage compared to cloud data centers
- Connectivity Variability: Intermittent network connections require resilient deployment and update mechanisms
- Security Complexity: Distributed infrastructure expands the attack surface, requiring comprehensive security measures
Cloud devops consulting services specializing in edge computing help organizations navigate these challenges, implementing solutions like:
- Kubernetes distributions optimized for edge (K3s, MicroK8s) that run on resource-constrained devices
- GitOps-based deployment pipelines that handle intermittent connectivity gracefully
- Edge-to-cloud data synchronization strategies that optimize bandwidth usage
- Zero-touch provisioning systems that enable automated device onboarding at scale
Trend #8: FinOps and Cloud Cost Optimization
As cloud spending reaches new heights in 2025, FinOps the practice of bringing financial accountability to cloud usage has become a critical component of DevOps strategies. Organizations are discovering that without proper cost management, cloud expenses can spiral out of control.
The FinOps Framework
FinOps establishes collaboration between finance, engineering, and business teams to optimize cloud spending:
Inform: Providing visibility into cloud costs with detailed allocation to teams, projects, and business units.
Optimize: Identifying and implementing cost saving opportunities without sacrificing performance or reliability.
Operate: Establishing governance policies and automation that prevent cost overruns while enabling innovation.
Cost Optimization Strategies
Modern cloud devops engineering services incorporate sophisticated cost optimization techniques:
| Strategy | Potential Savings | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Right-sizing resources | 20-40% | Low |
| Reserved instances and savings plans | 30-60% | Medium |
| Spot instances for fault-tolerant workloads | 60-90% | Medium |
| Auto-scaling based on demand | 25-45% | Low |
| Storage tiering and lifecycle policies | 40-70% | Low |
| Removing unused resources | 15-30% | Low |
| Architectural optimization | 30-70% | High |
Organizations implementing comprehensive FinOps practices report average cloud cost reductions of 35% while maintaining or improving service quality.
Automated Cost Governance
Leading organizations embed cost controls directly into their DevOps workflows:
- Budget alerts that notify teams when spending exceeds thresholds
- Policy enforcement that prevents deployment of non-compliant resources
- Cost estimation integrated into CI/CD pipelines before deployment
- Automated cleanup of temporary and unused resources
- Chargeback systems that allocate costs to responsible teams, creating accountability
Trend #9: Platform Engineering and Internal Developer Platforms
Platform Engineering has emerged as a distinct discipline in 2025, focused on building Internal Developer Platforms (IDPs) that abstract infrastructure complexity and enable developer self service. This trend represents a maturation of DevOps practices, creating golden paths that balance flexibility with standardization.
The Rise of Platform Engineering
Traditional DevOps often required developers to become infrastructure experts. Platform Engineering takes a different approach:
Abstraction Layers: Creating simplified interfaces that hide infrastructure complexity while providing necessary control.
Self-Service Capabilities: Enabling developers to provision resources, deploy applications, and access services without waiting for operations teams.
Standardization with Flexibility: Providing opinionated, pre configured solutions for common use cases while allowing customization when needed.
Developer Experience Focus: Optimizing workflows to minimize cognitive load and maximize productivity.
Components of Modern Internal Developer Platforms
Successful IDPs integrate several key components:
Service Catalogs: Curated collections of pre approved services, databases, and infrastructure components that developers can provision on demand.
Golden Path Templates: Pre configured project templates that incorporate best practices for security, observability, and deployment.
Unified Developer Portals: Single interfaces where developers access documentation, provision resources, monitor applications, and manage deployments.
Infrastructure Orchestration: Automated workflows that handle complex provisioning and configuration tasks behind simple interfaces.
Organizations building IDPs through cloud devops service partnerships report 50% reduction in developer onboarding time and 40% increase in deployment frequency.
For teams looking to optimize their DevOps workflows, understanding best practices for cloud environments provides valuable guidance.
Trend #10: Continuous Compliance and Automated Governance
Regulatory requirements continue to expand in 2025, with new data protection laws, industry specific compliance mandates, and security frameworks emerging globally. Modern DevOps cloud services must incorporate continuous compliance and automated governance to meet these challenges.
Compliance as Code
Similar to Infrastructure as Code, Compliance as Code codifies regulatory requirements into machine-readable policies that can be automatically enforced:
Policy Definition: Translating compliance requirements (GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, PCI-DSS) into executable code.
Continuous Validation: Automatically checking infrastructure configurations, application code, and runtime behavior against compliance policies.
Automated Remediation: Correcting non compliant configurations automatically or blocking deployments that violate policies.
Audit Trail Generation: Creating comprehensive, tamper-proof records of all changes and compliance checks for regulatory audits.
Governance Automation Tools
Modern governance platforms integrate with DevOps workflows:
- Open Policy Agent (OPA): General purpose policy engine that enforces rules across cloud platforms
- Cloud Custodian: Automated cloud governance and compliance enforcement
- HashiCorp Sentinel: Policy as code framework integrated with Terraform
- AWS Config/Azure Policy/GCP Policy Intelligence: Cloud-native compliance monitoring and enforcement
Organizations implementing automated governance through cloud devops consulting services reduce compliance violations by 85% and cut audit preparation time by 70%.
Trend #11: GitOps and Declarative Infrastructure Management
GitOps has evolved from a niche practice to a mainstream approach for managing cloud infrastructure and application deployments. In 2025, GitOps principles are being applied across the entire software delivery lifecycle, creating unprecedented levels of transparency and control.
Core GitOps Principles
GitOps treats Git repositories as the single source of truth for system state:
Declarative Description: Entire system state is described declaratively in Git repositories.
Version Control: All changes are committed to Git, creating complete audit trails and enabling easy rollbacks.
Automated Synchronization: Operators continuously compare actual system state to desired state in Git, automatically correcting drift.
Pull-Based Deployment: Instead of pushing changes to production, agents running in target environments pull changes from Git repositories.
GitOps in Practice
Modern cloud devops engineering services implement GitOps using specialized tools:
Flux: CNCF graduated GitOps operator for Kubernetes that automates deployments and ensures cluster state matches Git repository definitions.
Argo CD: Declarative GitOps continuous delivery tool with rich visualization and multi cluster support.
Jenkins X: Cloud native CI/CD platform built around GitOps principles for Kubernetes applications.
Rancher Fleet: GitOps-based deployment management for multi cluster Kubernetes environments.
Organizations adopting GitOps report 3x faster deployment frequencies, 60% reduction in deployment failures, and significantly improved disaster recovery capabilities.
Trend #12: Kubernetes and Container Orchestration Evolution
Kubernetes has become the de facto standard for container orchestration in 2025, but the ecosystem continues to evolve rapidly. Modern cloud devops service offerings increasingly center around Kubernetes expertise and specialized distributions.
Kubernetes Maturation
The Kubernetes ecosystem has matured significantly:
Simplified Operations: Managed Kubernetes services (EKS, AKS, GKE) handle control plane management, reducing operational complexity.
Enhanced Security: Pod security standards, network policies, and service mesh integration provide defense-in-depth.
Improved Developer Experience: Tools like Skaffold, Tilt, and DevSpace streamline local development and testing.
Ecosystem Consolidation: The proliferation of tools has given way to more integrated, opinionated platforms.
Specialized Kubernetes Distributions
Different use cases have driven the creation of specialized distributions:
- K3s: Lightweight Kubernetes for edge computing and resource constrained environments
- OpenShift: Enterprise platform with integrated CI/CD, developer tools, and operational features
- Rancher: Multi-cluster management platform that simplifies Kubernetes operations
- Tanzu: VMware’s enterprise Kubernetes platform with strong integration with traditional infrastructure
Service Mesh Adoption
Service meshes have moved from experimental to production ready, providing:
Traffic Management: Sophisticated routing, load balancing, and failure recovery for microservices.
Security: Mutual TLS encryption, authentication, and authorization between services.
Observability: Detailed metrics, distributed tracing, and logging for service to service communication.
Policy Enforcement: Centralized control over service behavior and access policies.
Popular service mesh implementations include Istio, Linkerd, and Consul Connect, each offering different trade offs between features and complexity.
Companies leveraging advanced Kubernetes strategies through cloud devops consulting services achieve 80% better resource utilization and 90% reduction in deployment related incidents.
Trend #13: Data-Driven DevOps and Analytics
The explosion of data generated by modern applications has created both challenges and opportunities for DevOps teams. In 2025, data driven DevOps leverages analytics to optimize every aspect of the software delivery lifecycle.
Metrics That Matter
Modern DevOps teams track sophisticated metrics beyond basic uptime and response time:
DORA Metrics: Deployment frequency, lead time for changes, mean time to recovery, and change failure rate provide comprehensive views of DevOps performance.
Value Stream Metrics: Tracking work items from conception through deployment reveals bottlenecks in the entire software delivery process.
Business Impact Metrics: Connecting technical metrics to business outcomes (revenue, user engagement, customer satisfaction) demonstrates DevOps value.
Resource Efficiency Metrics: Measuring resource utilization, cost per deployment, and infrastructure efficiency guides optimization efforts.
Analytics Driven Optimization
Advanced analytics enable continuous improvement:
- Deployment Success Prediction: Machine learning models predict deployment risk based on code changes, test coverage, and historical patterns
- Capacity Planning: Predictive analytics forecast resource needs based on business growth and usage trends
- Performance Optimization: Identifying performance bottlenecks through correlation analysis of metrics, logs, and traces
- Team Productivity Analysis: Understanding where developer time is spent to eliminate waste and improve efficiency
Organizations implementing data-driven DevOps practices report 45% improvement in deployment success rates and 30% reduction in infrastructure costs.
The convergence of DevOps and big data analytics creates powerful opportunities for organizations to optimize their entire technology stack.
Trend #14: Low Code/No Code Integration with DevOps
The rise of low code and no code platforms represents a democratization of software development. In 2025, forward thinking organizations are integrating these platforms into their DevOps workflows rather than treating them as separate ecosystems.
The Low Code Revolution
Low code/no code platforms enable:
Citizen Developers: Business users create applications without traditional programming skills, accelerating digital transformation.
Rapid Prototyping: Ideas can be validated through working prototypes in hours or days rather than weeks or months.
Reduced Development Backlog: Simple applications are built by business teams, freeing professional developers for complex challenges.
Faster Time to Market: Visual development interfaces dramatically reduce development time for certain application types.
DevOps for Low-Code Platforms
Professional cloud devops engineering services are extending DevOps practices to low code environments:
Version Control: Treating low code application definitions as code, storing them in Git repositories.
CI/CD Pipelines: Automated testing and deployment of low code applications through development, staging, and production environments.
Governance and Compliance: Ensuring low code applications meet security, performance, and regulatory requirements.
Integration Architecture: Connecting low code applications to enterprise systems through APIs and integration platforms.
Monitoring and Observability: Extending enterprise observability platforms to include low code applications.
Organizations successfully integrating low code platforms with DevOps practices achieve 60% faster delivery of business applications while maintaining enterprise grade quality and security standards.
Trend #15: Sustainability and Green DevOps
Environmental sustainability has become a business imperative in 2025, and DevOps practices are being optimized to reduce carbon footprints. Green DevOps focuses on minimizing the environmental impact of software development and operations.
The Carbon Cost of Computing
Cloud computing and software operations have significant environmental impacts:
- Data centers consume approximately 1% of global electricity
- Training large AI models can emit as much carbon as five cars over their lifetimes
- Inefficient code and infrastructure waste both money and energy
- E-waste from hardware refresh cycles creates environmental hazards
Green DevOps Practices
Modern cloud devops service providers incorporate sustainability measures:
Carbon-Aware Deployment: Scheduling workloads to run when and where renewable energy is available, reducing carbon emissions by 30 40%.
Efficiency Optimization: Right-sizing resources, eliminating waste, and optimizing code for energy efficiency.
Sustainable Architecture: Designing applications to minimize computational requirements and data transfer.
Green Metrics: Tracking carbon emissions alongside traditional performance and cost metrics.
Renewable Energy Selection: Choosing cloud regions and providers powered by renewable energy sources.
Organizations prioritizing green DevOps report both environmental benefits and cost savings, with many achieving 2030% reductions in cloud related carbon emissions while simultaneously reducing expenses.
Implementing Future Ready Cloud DevOps: Practical Steps
Understanding trends is valuable, but implementation delivers results. Organizations looking to modernize their DevOps cloud services should follow a structured approach.
Assessment and Strategy Development
Current State Analysis: Evaluate existing DevOps maturity, cloud architecture, and organizational capabilities.
Goal Definition: Establish clear objectives aligned with business outcomes (faster delivery, improved reliability, cost reduction, enhanced security).
Gap Identification: Determine the distance between current state and desired state across people, processes, and technology.
Roadmap Creation: Develop a phased implementation plan that delivers value incrementally while building toward long-term vision.
Building the Right Team
Successful DevOps transformation requires both internal capability development and strategic partnerships:
Internal Skill Development: Invest in training and certification for existing team members in cloud platforms, DevOps tools, and modern practices.
Strategic Hiring: Recruit specialized talent in areas like Kubernetes, security, and site reliability engineering.
Partner Selection: Engage cloud devops consulting services that provide expertise, accelerate implementation, and transfer knowledge to internal teams.
Culture Transformation: Foster collaboration, experimentation, and continuous learning across development and operations teams.
Technology Selection and Implementation
Platform Decisions: Choose cloud providers, Kubernetes distributions, and core tools based on specific requirements and existing investments.
Incremental Adoption: Implement new practices and tools gradually, starting with pilot projects that demonstrate value.
Automation First: Prioritize automation of repetitive tasks, focusing on areas with highest return on investment.
Continuous Improvement: Establish feedback loops that enable ongoing optimization based on metrics and team experiences.
Organizations partnering with experienced cloud devops engineering services accelerate their transformation journeys, often achieving in months what would take years with internal resources alone.
For comprehensive guidance on implementing DevOps effectively, exploring proven best practices provides a solid foundation.
Measuring Success: KPIs for Cloud DevOps Excellence
Effective DevOps requires measuring the right metrics. Organizations should track both technical and business KPIs to demonstrate value and guide continuous improvement.
Technical Performance Indicators
Deployment Frequency: How often code is deployed to production (leading organizations deploy multiple times per day).
Lead Time for Changes: Time from code commit to production deployment (high performers achieve under one hour).
Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR): Average time to restore service after an incident (target: under one hour).
Change Failure Rate: Percentage of deployments causing production issues (target: under 15%).
System Availability: Uptime percentage (modern cloud applications target 99.9% or higher).
Business Impact Metrics
Time-to-Market: Duration from concept to customer availability for new features.
Customer Satisfaction: Net Promoter Score (NPS) and customer satisfaction ratings influenced by application performance and feature delivery.
Revenue Impact: Direct correlation between DevOps improvements and business revenue growth.
Cost Efficiency: Infrastructure costs per user, per transaction, or per revenue dollar.
Innovation Capacity: Percentage of engineering time spent on new capabilities versus maintenance and firefighting.
Organizations implementing comprehensive DevOps metrics programs report 2.5x higher revenue growth compared to competitors with less mature practices.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Even with clear trends and best practices, organizations face obstacles when modernizing their cloud devops service capabilities.
Challenge #1: Cultural Resistance
Problem: Teams accustomed to traditional silos resist collaboration and shared responsibilities.
Solution:
- Establish cross-functional teams with shared goals and metrics
- Celebrate early wins that demonstrate DevOps value
- Provide training and support to ease transitions
- Lead by example from executive levels
Challenge #2: Legacy System Integration
Problem: Existing applications and infrastructure don’t align with modern DevOps practices.
Solution:
- Implement strangler fig pattern, gradually replacing legacy components
- Create APIs and abstraction layers around legacy systems
- Prioritize modernization based on business value and risk
- Use hybrid approaches that bridge old and new architectures
Challenge #3: Security and Compliance Concerns
Problem: Rapid deployment cycles appear to conflict with security and compliance requirements.
Solution:
- Integrate security into DevOps workflows (DevSecOps) from the beginning
- Automate compliance checking and policy enforcement
- Implement comprehensive audit trails and change tracking
- Partner with security teams to create secure golden paths
Challenge #4: Skill Gaps
Problem: Teams lack expertise in modern cloud platforms, containers, and DevOps tools.
Solution:
- Invest in structured training and certification programs
- Hire strategic specialists to fill critical gaps
- Engage cloud devops consulting services for knowledge transfer
- Create communities of practice for shared learning
Challenge #5: Tool Sprawl
Problem: Too many tools create complexity, integration challenges, and increased costs.
Solution:
- Establish tool evaluation and approval processes
- Consolidate around platforms that integrate multiple capabilities
- Standardize on core toolchains while allowing flexibility for edge cases
- Regularly review and retire underutilized tools
Organizations that proactively address these challenges through structured change management and strategic partnerships achieve DevOps transformation success rates 3x higher than those that don’t.
The Role of AI and Generative AI in DevOps Evolution
Artificial intelligence, particularly generative AI, is creating unprecedented opportunities for DevOps automation and optimization in 2025. The integration of generative AI in digital marketing demonstrates the broader applicability of these technologies across business functions.
AI-Powered Code Generation and Review
Generative AI tools are transforming how developers write and review code:
Automated Code Completion: AI assistants suggest entire functions, classes, and modules based on context and requirements.
Intelligent Code Review: Machine learning models identify potential bugs, security vulnerabilities, and performance issues before human review.
Test Generation: AI creates comprehensive test suites automatically based on code analysis and usage patterns.
Documentation Creation: Generative AI produces clear, accurate documentation from code and comments.
Infrastructure Optimization Through AI
AI is optimizing cloud infrastructure management:
- Predictive Auto-Scaling: ML models forecast demand and scale resources proactively rather than reactively
- Cost Optimization: AI identifies cost saving opportunities across complex multi-cloud environments
- Security Threat Detection: Behavioral analysis identifies potential security threats that rule based systems miss
- Performance Tuning: AI continuously optimizes configurations for maximum performance and efficiency
Organizations leveraging AI-driven innovation in their DevOps practices report 50% reduction in manual tasks and 40% improvement in system performance.
Conversational DevOps Interfaces
Natural language interfaces are making DevOps tools more accessible:
ChatOps: Teams interact with DevOps tools through chat interfaces, lowering barriers to entry and improving collaboration.
Voice-Activated Operations: Engineers can query system status, trigger deployments, and respond to incidents using voice commands.
Natural Language Queries: Instead of learning complex query languages, teams can ask questions in plain English and receive insights.
AI Assisted Troubleshooting: Conversational AI guides engineers through diagnostic and resolution processes based on symptoms and context.
Future Outlook: What’s Next for Cloud and DevOps?
Looking beyond 2025, several emerging trends will shape the next evolution of DevOps cloud services:
Quantum Computing Integration
As quantum computing becomes more accessible, DevOps practices will need to evolve to support:
- Hybrid classical quantum application architectures
- Specialized deployment and orchestration for quantum workloads
- New testing paradigms for quantum algorithms
- Integration of quantum capabilities into existing applications
Autonomous Operations
The progression toward fully autonomous systems will continue:
- Self optimizing infrastructure that requires minimal human intervention
- AI systems that make complex architectural decisions
- Automated incident response that resolves most issues without human involvement
- Continuous architecture evolution driven by machine learning
Extended Reality (XR) DevOps
As AR, VR, and mixed reality applications become mainstream:
- DevOps practices will extend to support immersive application deployment
- New testing frameworks for spatial computing experiences
- Infrastructure optimized for real-time 3D rendering and low-latency interaction
- Edge computing integration for XR workload distribution
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Integration
Blockchain technology will influence DevOps practices:
- Immutable audit trails for compliance and security
- Decentralized application deployment and orchestration
- Smart contract based automation and governance
- Distributed identity and access management
Organizations staying ahead of these trends through partnerships with innovative cloud devops engineering services will maintain competitive advantages as technology continues its rapid evolution.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Cloud and DevOps
The convergence of cloud computing and DevOps has fundamentally transformed how organizations build, deploy, and operate software. The trends outlined in this article from AI powered automation to sustainability-focused practices represent not just incremental improvements but revolutionary changes in how technology enables business value.